EPSS Score – Exploit Prediction Scoring System
EPSS Score (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) has established itself as an essential tool in the field of cybersecurity, allowing organizations to understand vulnerabilities and their exploitation potential.
EPSS Score (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) has established itself as an essential tool in the field of cybersecurity, allowing organizations to understand vulnerabilities and their exploitation potential.
In this blog article, we will define and explore the workings of this score, its concrete advantages and its integration into security strategies.
How does the EPSS score work?
EPSS is a rating system that estimates the likelihood that a software vulnerability will be exploited in the next 30 days. This is a valuable tool for IT security teams because it can help them prioritize their vulnerability remediation efforts.
The EPSS score is a percentage between 0 and 1. 0 indicates that the vulnerability is very unlikely to be exploited and 1 indicates that it is very likely that it will be exploited.
The score is calculated using a statistical model that takes into account a number of factors, including:
- The characteristics of the vulnerability: These include factors such as the type of vulnerability, the severity of the vulnerability, and the number of software affected.
- Exploitation history: This includes information on whether the vulnerability has been exploited in the past and how often it was exploited.
- Threat intelligence: This is information about the threat actors who are likely to exploit the vulnerability and their motivations.
- Availability of an exploit: The existence of an accessible public exploit significantly increases the risk of exploitation, hence impacting the EPSS score.
- The intrinsic severity of the vulnerability: Critical flaws, with potentially devastating impacts, generally obtain higher EPSS scores.
- The attack vector: Remote accessibility, facilitating exploitation, increases criticality and therefore the EPSS score.
- Business impact: Critical systems and sensitive data are preferred targets, which results in a higher EPSS score.
In addition to the EPSS score, the system also provides an EPSS percentile. The EPSS percentile indicates the percentage of vulnerabilities for which the EPSS score is less than or equal to the EPSS score of the vulnerability in question. For example, an EPSS percentile of 85% indicates that the vulnerability is more likely to be exploited than 85% of other vulnerabilities analyzed.
EPSS can be used in different ways to prioritize vulnerabilities.
- A common approach is to rank vulnerabilities by their EPSS score , remediating vulnerabilities that have the highest score first.
- Another approach is to set an EPSS score threshold and only remediate vulnerabilities that score above that threshold.
EPSS is a valuable tool for IT security teams, but it is important to use it in conjunction with other factors when prioritizing vulnerabilities.

Why is the EPSS score important?
The importance of the EPSS score lies in its ability to provide security managers with a more realistic view of the actual risk posed by a vulnerability. Indeed, CVSS does not take into account factors such as the availability of an exploit, the motivation of attackers or the specificity of the target environment.
EPSS, on the other hand, relies on data from a variety of sources, such as Common Vulnerabilities & Exposures (CVE) and actual exploit information, to estimate the likelihood that a vulnerability will actually be exploited.
Why combine EPSS and CVSS?
We combine the CVSS score and the EPSS to have a better assessment of the IT security risk.
- CVSS measures severity: Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) assigns a score based on the ease of exploitation and potential impact of a vulnerability. It is an objective measure of the inherent severity of a security breach.
- EPSS measures the probability of exploitation: The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) is a probabilistic value that reflects the chance that exploit code is available for a given vulnerability. It takes into account factors like exploit history and attacker activity.
By combining these two measures, we obtain a more complete view of risk. CVSS tells you the potential severity of damage if the vulnerability is exploited, while EPSS tells you how likely it is to actually happen.
Explanation with a diagram of the interest of mixing EPSS and CVSS
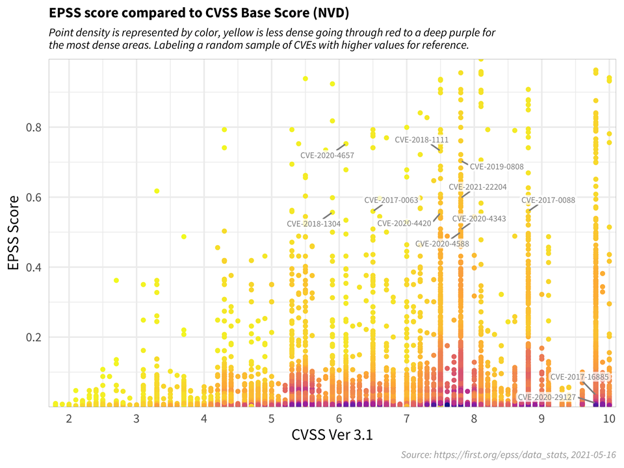
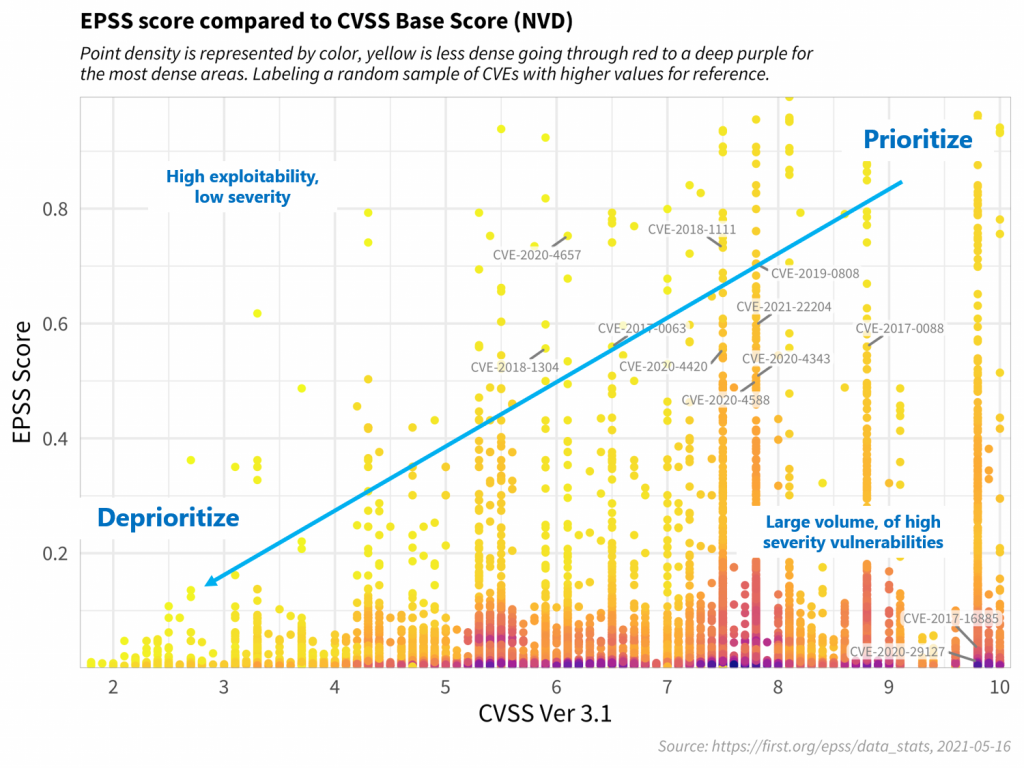
In the graph above, the CVSS and EPSS scores of multiple CVEs have been correlated.
On the abscissa are the CVSS scores on a scale of 0 to 10, the closer we get to 0, the less severe the vulnerability, the closer the score gets to 10, the more severe the flaw is considered.
On the ordinate are the EPSS scores, on a scale of 0 to 1. An EPSS score close to 0 indicates a low probability of exploitation, a score close to 1 indicates a very high probability of exploitation.
In this graph, each yellow point indicates a CVE, so colors closer to purple indicate that many CVEs are represented at the same threshold.
Thus, we can notice that many CVEs with very high CVSS scores actually have quite low EPSS scores.
It is therefore logical to prioritize CVE vulnerabilities having both high CVSS scores but also high EPSS exploitation scores.
The advantages of using the EPSS score
EPSS distinguishes itself from other vulnerability rating systems by several major advantages, which make it a valuable tool for managing security vulnerabilities.
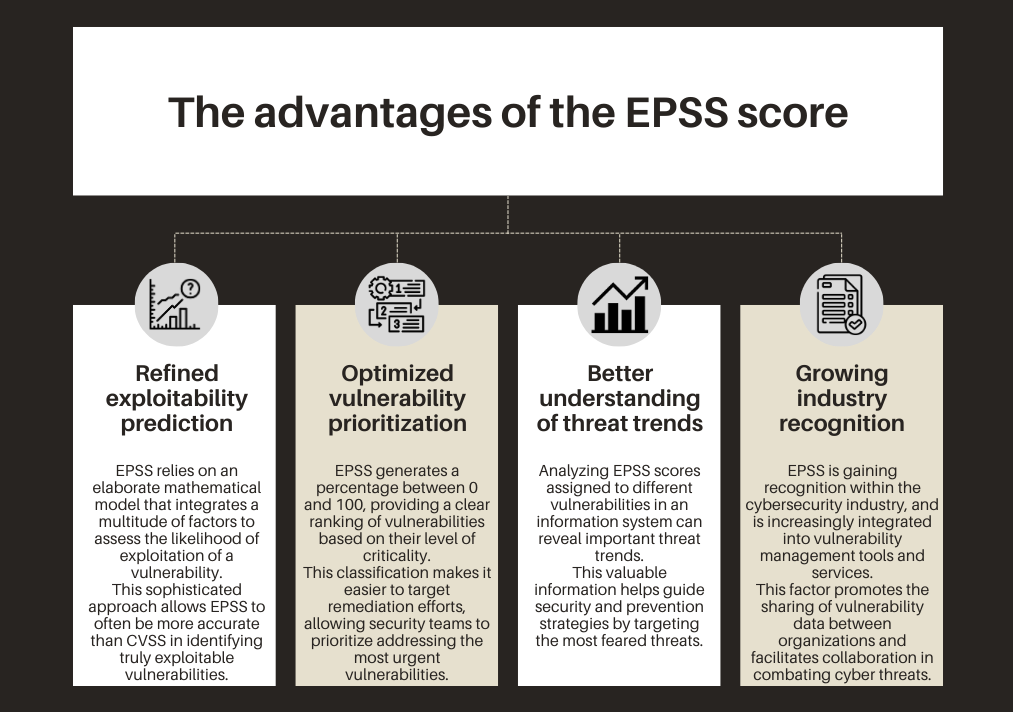
1. Refined exploitability prediction
EPSS relies on an elaborate mathematical model that integrates a multitude of factors to assess the likelihood of exploitation of a vulnerability.
This sophisticated approach allows EPSS to often be more accurate than CVSS in identifying truly exploitable vulnerabilities.
Let’s take the example of a recent vulnerability affecting commonly used software. The CVSS could give it a high score because of its potential impact. However, if the EPSS analysis reveals that the conditions necessary for its operation are rare or complex, it will receive a lower score, better reflecting the actual risk.
2. Optimized vulnerability prioritization
EPSS generates a percentage between 0 and 100, providing a clear ranking of vulnerabilities based on their level of criticality.
This classification makes it easier to target remediation efforts, allowing security teams to prioritize addressing the most urgent vulnerabilities.
Imagine an information system with dozens of vulnerabilities detected. The EPSS score allows these vulnerabilities to be quickly sorted and focused first on those presenting an imminent exploitation risk, thus optimizing the allocation of resources dedicated to security.
3. Better understanding of threat trends
Analyzing EPSS scores assigned to different vulnerabilities in an information system can reveal important threat trends.
For example, if a significant number of vulnerabilities have a high EPSS score, this may indicate that the system is particularly vulnerable to a specific type of attack.
This valuable information helps guide security and prevention strategies by targeting the most feared threats.
Consider an organization seeing an increase in high EPSS scores for email- related breaches. This suggests an increased risk of phishing or email- delivered malware attacks. The organization can then strengthen its messaging security measures, educate its employees about the risks and implement more sophisticated filtering solutions.
4. Growing industry recognition
EPSS is gaining recognition within the cybersecurity industry, and is increasingly integrated into vulnerability management tools and services.
This factor promotes the sharing of vulnerability data between organizations and facilitates collaboration in combating cyber threats.
The growing adoption of EPSS helps pool efforts and increase the overall effectiveness of cybersecurity.
Summary of EPSS Score Advantages
In addition to the above points, it is important to emphasize that the EPSS is a constantly evolving system.
In summary, EPSS offers a set of advantages that position it as an essential tool for vulnerability management. Its ability to accurately predict exploitability, prioritize remediation actions, and provide insights into threat trends makes it an indispensable asset for today’s security teams.
The limits of the EPSS score
The Exploitation Forecast Scoring System (EPSS) is a valuable tool to help cyber defenders prioritize vulnerability remediation efforts. However, it is crucial to understand its limitations before using it.
Focus on probability of exploitation, not severity
The EPSS score only measures the probability of exploitation of a vulnerability, omitting the severity of its potential consequences. A vulnerability with a high EPSS score may be less serious than one with a low score if the latter results in greater damage if exploited.
Reliability based on historical data
EPSS relies on historical data, which can limit its accuracy for new or under-exploited vulnerabilities.
Statistical nature of the model
Since EPSS is a statistical model, it is always possible that a vulnerability with a low EPSS score will be exploited, and vice versa.
Lack of consideration of specific environmental factors
The EPSS does not take into account the particularities of each organization, such as their risk profile or security practices.
Our advice for using the EPSS score
Combine EPSS with other vulnerability management tools
Severity rating systems like CVSS help assess the severity of a vulnerability’s potential impacts, providing a more comprehensive view for prioritization.
Threat analysis tools help identify the threats most relevant to the organization, helping to prioritize vulnerabilities exploitable by these attack vectors.
Vulnerability management solutions can automate the process of scanning, detecting and prioritizing vulnerabilities, making EPSS data management easier.
Take into account the organizational risk profile
Organizations exposed to certain types of attacks, such as ransomware attacks, can prioritize vulnerabilities exploitable by these vectors.
Regulated industries may have specific vulnerability management requirements to consider when prioritizing.
The size and maturity of the organization can influence the ability to manage a large number of vulnerabilities, impacting prioritization.
Continuously update threat intelligence
The EPSS is regularly updated with new information on vulnerabilities and exploits. It is crucial to use the latest version available and stay informed of new threats affecting the organization.
Threat intelligence sources like CERT alerts or vulnerability research reports can help identify new threats and update priorities accordingly.
Use EPSS as a decision-making tool, not as a definitive solution
EPSS helps identify the most urgent vulnerabilities to address, but professional judgment and contextual analysis are essential before making decisions.
Factors such as available resources, potential impacts on operations, and dependencies between systems should be considered to refine priorities.
Clear communication between security teams and other stakeholders is essential to ensure that vulnerability remediation decisions are aligned with the organization’s overall goals.
