Cyber Threat Intelligence -CTI
In today’s ever-changing digital landscape, organizations face a growing array of sophisticated cyber threats. Faced with this growing danger, Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) has emerged as an essential tool for the protection of information systems and sensitive data.
In today’s ever-changing digital landscape, organizations face a growing array of sophisticated cyber threats. Faced with this growing danger, Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) has emerged as an essential tool for the protection of information systems and sensitive data.
What are the objectives of Cyber Threat Intelligence?
1. Understand and anticipate threats
Malicious actor mapping
Malicious actor mapping involves profiling hacker groups, malicious individuals, and criminal organizations, analyzing their motivations, targets, tools, and techniques.
This makes it possible to understand the modus operandi of the different actors and to anticipate their actions.
Monitoring Emerging Threats
Monitoring emerging threats involves monitoring underground forums, social networks and other intelligence sources to identify new vulnerabilities, malware and attack techniques.
The end goal is to enable organizations to prepare for threats before they are widely exploited.
Analysis of cyberattack trends
This involves examining historical cyberattack data to identify trends, such as:
- Most targeted sectors,
- Most common types of attacks,
- Most used attack vectors.
The goal is to prioritize organizations’ defense efforts and allocate their resources more efficiently.
2. Improve intrusion detection and incident response
Identifying Indicators of Compromise (IOC)
Identifying indicators of compromise helps collect specific artifacts, such as malicious IP addresses, malicious file hashes, and phishing URLs, that indicate that an intrusion has occurred or is in progress.
IOCs can be used to configure security systems to detect and block attacks.
Enriching security systems with threat intelligence
This involves integrating CTI information into security systems, such as:
- Firewalls,
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS),
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
Integrating CTI information into security systems allows you to better understand the context of attacks and make more accurate decisions.
Automating Incident Response
Incident response automation is the implementation of automated processes to respond to cybersecurity incidents, such as:
- Quarantine of infected systems,
- Closure of compromised accounts,
- Notification of authorities.
This automation helps reduce response time and limit the damage caused by a cyberattack.
3. Prioritize security efforts and make informed decisions
Cyber risk assessment
It involves analyzing an organization’s assets, vulnerabilities and potential threats to determine its overall cyber risk level.
This helps prioritize security measures and ensure resources are allocated to the most critical areas.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Security Controls
It is essential to regularly test and evaluate an organization’s security controls to ensure they are effective against today’s threats.
And this with the aim of identifying security vulnerabilities and taking corrective measures.
Allocation of security resources
Allocating security resources to different projects and initiatives based on the level of risk and the value of the assets protected helps maximize the ROI of security investments.
4. Support business continuity and resilience
Development of incident response plans
Documented plans describing the steps to follow in the event of a cyber attack (communication, system restoration, disaster recovery) allow organizations to respond quickly and effectively.
Implementation of data protection measures
Implementing security controls is useful to protect sensitive data against data leaks and cyberattacks, such as encryption, access control and identity and access management (IAM), and thus minimize the impact of a data breach.
Cyber Resilience Testing
Cyber incident simulation exercises are a valuable tool for strengthening an organization’s cybersecurity posture and increasing its resilience to ever-evolving threats.
By taking a proactive approach and learning from exercises, organizations can minimize the potential impact of cyberattacks and protect their critical assets.
What are the CTI’s sources of information?
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) is crucial for organizations of all sizes to protect against sophisticated and evolving attacks.
By collecting and analyzing information from a variety of sources, businesses can better understand potential threats, implement appropriate defenses, and respond quickly to incidents.
CTI information sources can be classified into two broad categories:
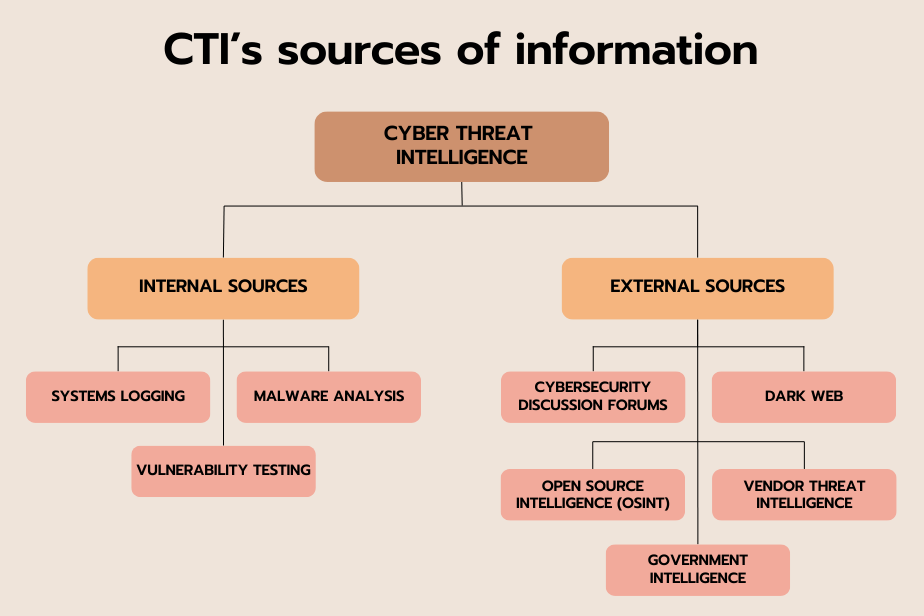
1. Internal sources
Systems logging
Logs from information systems, firewalls, IDS/IPS and other security devices provide detailed information on network and user activities, helping to detect suspicious behavior and potential intrusions.
Malware analysis
Examining malware captured in incidents or obtained for analysis reveals new attack techniques, valuable indicators of compromise (IoCs), insights into threat actors and their motivations.
Vulnerability testing
Regular scans of systems and applications help identify security vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers, enabling remediation efforts to be prioritized and attack risk reduced.
2. External sources
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
OSINT leverages publicly available information on the Internet, such as social networks, online forums, malware repositories, research reports, and specialized databases, to identify emerging threats, known vulnerabilities, and the activities of malicious actors.
Vendor Threat Intelligence
Security vendors often share information about the threats they observe in their networks and with their customers, providing a holistic perspective on trends and ongoing malicious campaigns.
Government Intelligence
Government agencies and international organizations collect and share critical intelligence information on high-level cyber threats, nation-state activities, and targeted cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity Discussion Forums
Online cybersecurity forums and communities allow researchers, professionals, and enthusiasts to share knowledge, analysis, and findings regarding recent threats, vulnerabilities, and defense techniques.
Dark web
The dark web, while harboring illegal activity, can also contain valuable threat intelligence, such as the sale of malware, stolen data and hacking tools, providing insight into cybercriminals’ tools and tactics.
How does Cyber Threat Intelligence fit into security operations?
Protection against known and emerging threats
One of the key benefits of CTI integration is its ability to directly power critical security systems, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems. (IPS). This integration allows for several major improvements:
- Improved threat detection: Security systems are equipped with more comprehensive information about known threats, including indicators of compromise (IOCs) and malicious actors’ tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs). This allows them to more effectively identify and block attacks, even sophisticated and novel ones.
- False Positive Reduction: Using CTI allows security systems to more accurately differentiate between real threats and legitimate activity, reducing the number of irrelevant alerts and wasting valuable resources for security analysts.
- Critical Incident Prioritization: By providing contextual threat information, CTI enables incident response teams to quickly prioritize incidents based on severity and actual risk to the organization. This ensures that the most critical incidents receive the necessary attention and resources as a priority, thereby limiting the overall impact of cyberattacks.
Improved decision making and awareness
CTI is not limited to the technical protection of systems. It also plays a crucial role in raising awareness and empowering key players within the organization:
- Informed strategic decisions: Executives and security managers can base their decisions on hard data and in-depth analyzes of current threats, enabling more efficient allocation of resources and better risk management.
- Increased employee awareness: Providing relevant and tailored CTI information to employees increases their vigilance against common online threats, such as phishing, malware and social engineering attacks. This reduces the likelihood of human errors that could compromise the security of the organization.
Collaboration and information sharing
CTI is not just an individual tool for each organization. It is also most effective when shared and used collaboratively:
- Threat Knowledge Sharing: Organizations can collaborate to collect and share information about emerging threats, critical vulnerabilities, and ongoing malware campaigns. This allows all stakeholders to benefit from a global view of the cyber threat landscape and to implement collective countermeasures.
- Combating large-scale cyberattacks: Sharing information about ongoing attacks allows organizations to alert each other and take preventative measures to limit the spread of malware or intrusions.
- Improved cyber threat research: Collaboration between organizations and security researchers can accelerate the discovery of new threats and the development of protective solutions.
What are the advantages of CTI?
The benefits of CTI are numerous and can apply to all types of organizations, regardless of their size or sector of activity.
1. Attack Prevention
The CTI makes it possible to identify:
- Potential threats before they strike, giving organizations time to put countermeasures in place and protect themselves.
- Vulnerabilities in systems and applications, which can then be patched before they are exploited by attackers.
2. Cost reduction
A cyberattack can be costly to an organization, both in terms of financial losses and damage to its reputation. CTI can help reduce these costs by preventing attacks and limiting the impact of attacks that do occur.
3. Improved security posture
The CTI can:
- Helping organizations improve their overall security posture by giving them better visibility into the threats they face. This information can then be used to guide security efforts and ensure the most appropriate security controls are in place.
- Be used to improve security awareness training for employees, giving them real-world examples of the threats they may face.
4. More informed decision making
The CTI allows you to:
- Helping leaders make more informed cybersecurity decisions by providing them with the information they need to understand the risks their organization faces. This information can then be used to prioritize security initiatives and allocate resources more efficiently.
- Measure the effectiveness of security programs, allowing leaders to track their progress and make adjustments as necessary.
5. Gaining a competitive advantage
In an ever-changing threat landscape, organizations with a robust CTI program can gain a competitive advantage by being better prepared to defend against cyberattacks.
