What is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate, an acronym for Secure Sockets Layer, is a crucial element in the security of online exchanges. A true digital sentinel, it ensures the protection of sensitive user data during their interactions with websites.
An SSL certificate, an acronym for Secure Sockets Layer, is a crucial element in the security of online exchanges. A true digital sentinel, it ensures the protection of sensitive user data during their interactions with websites.
What is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate is a digital file stored on a website’s server.
Role of SSL certificates
SSL certificates and SSL/TLS exchanges play a crucial role in the security of communications on the Internet. They allow you to:
- Encrypt data and protect it from prying eyes: Encrypted data can only be decrypted by the server that has the corresponding private key.
- Authenticate the identity of the website or server: The browser checks the SSL certificate to ensure that it is issued by a trusted authority and that it corresponds to the website it wishes to visit.
- Keep communications private and confidential: Data exchanged between the browser and the server cannot be intercepted and decrypted by third parties.
Composition of an SSL certificate
The SSL certificate is made up of several key elements:
- Public key: A mathematical key used to encrypt data sent to the server. This key is accessible to everyone.
- Private key: A mathematical key used to decrypt data received from the server. This key is kept secret by the server.
- Identity of owner: The name of the company or individual who owns the certificate. This could be the website domain name, organization name, or a username.
- Certificate Authority: A trusted organization that has verified the identity of the owner and issued the certificate. This information is also accessible to everyone.
How does an SSL certificate work?
An SSL certificate is an essential element for secure online communications. It acts as a digital passport that helps verify the identity of a website and encrypts data transmitted between the web browser and the web server.
Here is an explanation of how it works:
SSL/TLS exchange
When you visit a website secured by an SSL certificate, an exchange called a “handshake” takes place between your browser and the web server. This exchange makes it possible to establish a secure connection and guarantee the identity of the website.
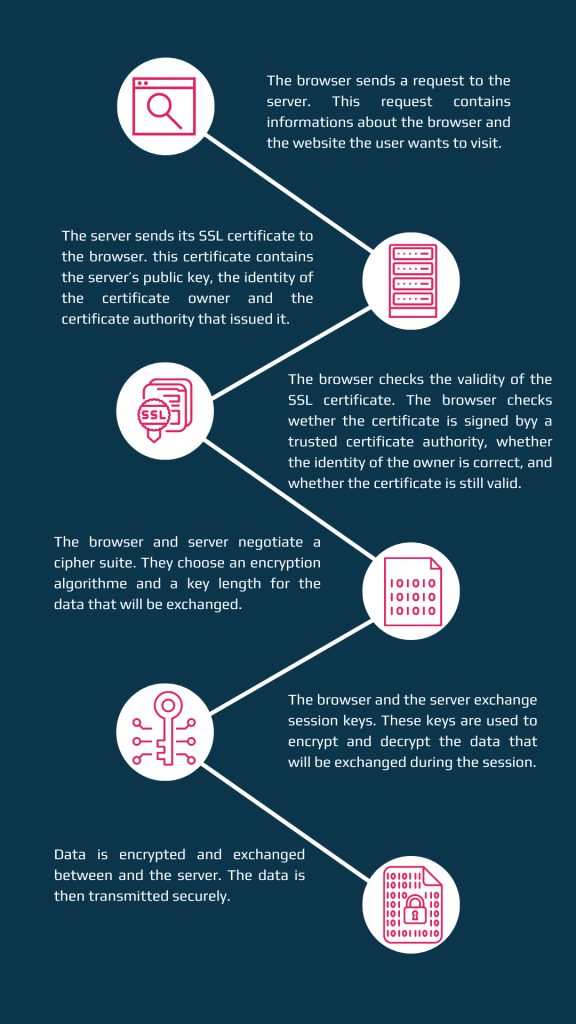
Here are the SSL/TLS handshake steps in detail:
- The browser sends a request to the server. This request contains information about the browser and the website the user wants to visit.
- The server sends its SSL certificate to the browser. This certificate contains the server’s public key, the identity of the certificate owner and the certificate authority that issued it.
- The browser checks the validity of the SSL certificate. The browser checks whether the certificate is signed by a trusted certificate authority, whether the identity of the owner is correct, and whether the certificate is still valid.
- The browser and server negotiate a cipher suite. They choose an encryption algorithm and a key length for the data that will be exchanged.
- The browser and the server exchange session keys. These keys are used to encrypt and decrypt the data that will be exchanged during the session.
- Data is encrypted and exchanged between the browser and the server. The data is then transmitted securely.
The different types of SSL certificate
Choosing the right type of SSL certificate for your website is crucial to ensuring the security of your data and the trust of your users. Here’s a detailed guide to the three main types of SSL certificates, as well as other less common types:
Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificates
- Easiest and cheapest to obtain.
- Only checks domain ownership.
- Displays a gray padlock in the address bar with the domain name.
- Ideal for websites that do not collect sensitive data.
- Examples: Personal blogs, news websites, small business websites
Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificates
- More expensive than a DV certificate.
- Verifies organization identity and domain name.
- Displays a green padlock in the address bar with the organization name.
- Ideal for websites that collect sensitive data.
- Examples: E-commerce websites, banking websites, contact form websites.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
- The most expensive and most secure type of certificate.
- Verifies the identity of the organization very thoroughly.
- Displays a green padlock in the address bar with the organization name and certificate authority name.
- Ideal for websites that collect very sensitive data.
- Examples: government websites, investment banking websites, healthcare websites.
| Criteria / SSL Certificates | DV Domain Validation | OV Organization Validation | EV Extended Validation |
| Price | — | Medium | ++ |
| Verification | Domain ownership | Organization identity + Domain name | Extensive organizational identity |
| Display | Gray padlock + Domain name | Green padlock + Name of the organization | Green padlock + Name of the organization + Certificate Authority name |
| For who ? | Sites not collecting data | Sites collecting sensitive data | Sites collecting very sensitive data |
| Examples | Blog / Press / Informational sites | E-commerces sites / Banking sites / Contact forms | Governement sites / Health sites |
Other types of SSL certificates
Wildcard SSL Certificates
- Secure a main domain and all its subdomains.
- Useful for websites with multiple subdomains, like WordPress blogs.
Multi-domain SSL certificates
- Secure multiple domains with a single certificate.
- Perfect for businesses that manage multiple websites.
Why use an SSL certificate?
Data security
An SSL certificate is an essential element for the security of a website and the protection of user data. It encrypts data transmitted between a website and users’ browsers, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it. This is especially important for websites that collect sensitive information, such as:
- Payment information: credit card numbers, bank account numbers, PIN codes.
- Login information: usernames, passwords.
- Personal data: names, addresses, telephone numbers, dates of birth.
In addition to protecting sensitive data, using an SSL certificate can help comply with various regulations, such as GDPR, which require websites that collect personal data to have appropriate security measures in place.
User Trust
When users visit a website secured by an SSL certificate, a green padlock appears in their browser’s address bar. This symbol indicates that the connection is secure and users can trust the website to protect their data.
Improved SEO
Google and other search engines favor websites that use SSL certificates in their search results. This means that using an SSL certificate can help you improve your website’s ranking and make it more visible to searchers.
Better user experience
Websites that use SSL certificates can also enjoy other benefits, such as:
- Faster page loading: HTTP/2, which is faster than HTTP/1.1, is only available to websites that use an SSL certificate.
- Modern Browser Compatibility: Most modern web browsers no longer support websites that do not use an SSL certificate.
How do I know if a site has a valid SSL certificate?
There are several ways to find out if a website has an SSL certificate:
- If the URL starts with https://, it means the website is using an SSL certificate.
- If the URL starts with http://, it means the website is not using an SSL certificate.
Find the padlock in the address bar
- If you see a green padlock in your browser’s address bar, it means that the website is using a valid SSL certificate.
- If you don’t see a padlock, it means the website is not using an SSL certificate or the certificate is invalid.
Click on the padlock
If you click the padlock, you can view additional information about the SSL certificate, such as the certificate authority that issued it and the expiration date.
Use an SSL Certificate Testing Tool
There are online tools that allow you to test the security of an SSL certificate.
You can use these tools to check if an SSL certificate is valid and if it uses strong encryption algorithms.
Choose HTTPCS to obtain an SSL certificate
HTTPCS is a website that offers SSL certificates at affordable prices. It offers a wide range of certificates, including DV, OV and EV certificates.
Here are some advantages of using HTTPCS to obtain an SSL certificate:
- Affordable Prices: HTTPCS offers SSL certificates at very competitive prices.
- Wide selection of certificates: They offer a wide range of certificates to meet all needs.
- Easy to use: The ordering and installation process is quick and easy.
- Customer Support: They offer excellent and responsive customer support.
