Zero Trust – What is it?
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity strategy that aims to secure organizations by eliminating implicit trust and continuously validating every step of a digital interaction.
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity strategy that aims to secure organizations by eliminating implicit trust and continuously validating every step of a digital interaction.
This model is based on the fundamental principle that no user, device or application should be granted intrinsic trust, even if they are inside the network perimeter.
What are the principles of the Zero Trust approach?
The Zero Trust approach is based on several principles which are:
- Never trust, always verify.
- Control access constantly.
- Minimize the attack perimeter.
- Secure data.
- Ensure visibility and traceability.
- Automate incident responses.
- Constantly test and improve.
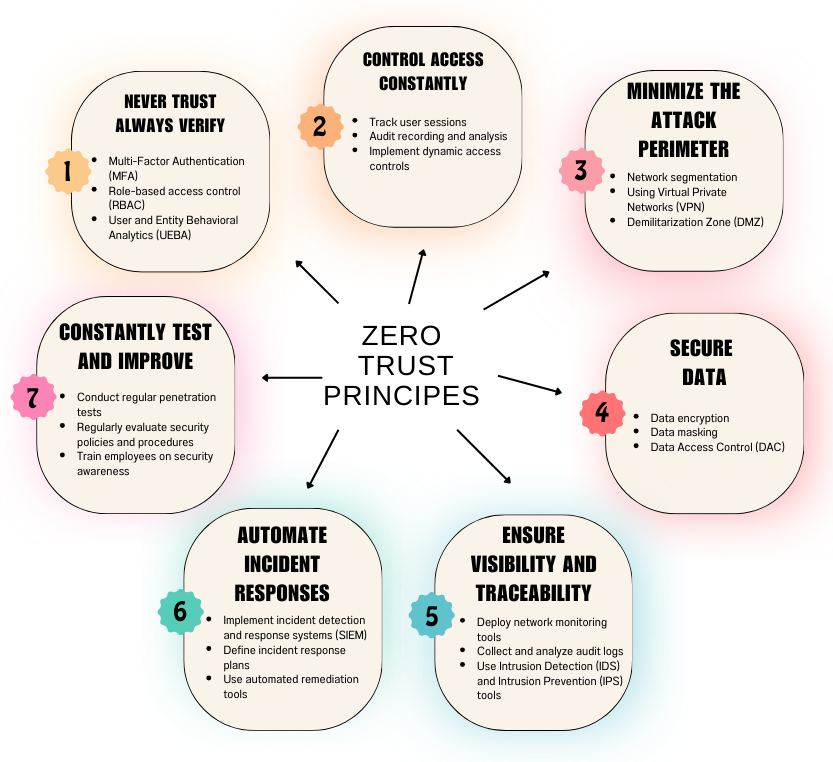
1. Never trust, always verify
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Go beyond passwords by requiring additional authentication factors, such as fingerprints, security codes sent via SMS, or authenticator apps.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Limit access to resources based on each user’s role within the organization.
- User and Entity Behavioral Analytics (UEBA): Monitor user and device activities to detect abnormal behavior that could indicate a threat.
2. Control access constantly
- Track user sessions: Monitor user activity in real time and automatically log them out after a period of inactivity.
- Audit recording and analysis: Record all user and system actions so you can review them in the event of an incident.
- Implement dynamic access controls: Adjust access permissions based on context, such as time of day, user location, or type of device used.
3. Minimize the attack perimeter
- Network segmentation: Divide your network into smaller segments and apply separate security controls to each segment.
- Using Virtual Private Networks (VPN): Secure remote connections by creating encrypted VPN tunnels.
- Demilitarization Zone (DMZ): Place critical resources in a separate network zone to isolate them from the rest of the network.
4. Secure data
- Data encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Data masking: Hide sensitive information in data, such as credit card numbers or home addresses.
- Data Access Control (DAC): Limit access to data to users and applications that need it.
5. Ensure visibility and traceability
- Deploy network monitoring tools: Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Collect and analyze audit logs: Maintain detailed records of all user and system activity.
- Use Intrusion Detection (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention (IPS) tools: Identify and block malicious intrusion attempts.
6. Automate incident responses
- Implement incident detection and response systems (SIEM): Automate the collection and analysis of incident data for faster response.
- Define incident response plans: Define clear procedures for responding to different types of security incidents.
- Use automated remediation tools: Automate remediation tasks, such as resetting passwords or updating software.
7. Constantly test and improve
- Conduct regular penetration tests: Simulate cyberattacks to identify security vulnerabilities.
- Regularly evaluate security policies and procedures: Make sure they are always up to date and effective.
- Train employees on security awareness: Help employees identify and report potential threats.
How to implement a Zero Trust approach?
Faced with the proliferation of sophisticated cyber threats, businesses of all sizes are rushing to adopt a Zero Trust security approach. This security model abandons the traditional perimeter concept and considers that each access to resources must be constantly verified and authenticated.
If you are embarking on this crucial process, this complete guide will accompany you step by step.
1. Establish a tailor-made Zero Trust strategy
Dive into your specific organizational context to define a tailored Zero Trust strategy. This involves:
- Map your sensitive assets: Identify all critical data and systems that need to be protected.
- Identify users and their access needs: analyze who needs access to what resources and when.
- Assess potential risks: Understand the threats you face and possible attack vectors.
2. Master the fundamental pillars of Zero Trust
The founding principle of Zero Trust is “never trust implicitly, always verify”. Translate this principle into concrete actions:
- Robust authentication: Go beyond traditional passwords and adopt MFA (multi-factor) solutions based on tokens, biometrics or behavioral technologies.
- Granular authorization: Apply the principle of least privilege (PoLP) by granting users only the access necessary to complete their tasks.
- Network segmentation: Divide your network into smaller, controllable areas to limit the spread of intrusions.
- Always-on visibility and control: Monitor access, activity, and configuration changes in real time to detect suspicious behavior.
3. Implement Zero Trust with concrete examples
Let us illustrate these principles with practical cases:
Scenario 1: Access to a cloud application
An employee accesses a cloud application containing sensitive data. In a Zero Trust approach:
- Authentication: he authenticates via his password and an additional code sent to his smartphone.
- Authorization: he only has access to the data and functionalities necessary for his work, and not to the entire system.
- Monitoring: Its activity is monitored to detect any suspicious behavior. In the event of an anomaly, access is suspended.
Scenario 2: Access to the internal network from a personal device (BYOD)
An employee uses their personal device to access the company’s internal network. Zero Trust allows:
- Authentication: The device is authenticated and verified to ensure it complies with security policies.
- Access controlled: Device access is limited to authorized resources, and sensitive data is not downloaded to the device.
- Protection against malware: The device is scanned for malware and other threats before accessing the network.
4. Gradual deployment and continuous adaptation
Zero Trust is an iterative process:
- Start with the critical areas: identify the most sensitive areas and focus your efforts on securing them.
- Expand gradually: Roll out Zero Trust to the rest of your organization as you gain experience and resources.
- Continuously adapt: Stay informed of new threats and vulnerabilities, and adjust your strategy accordingly.
What are the advantages of the Zero Trust approach?
Adopting a Zero Trust approach to network security offers a multitude of significant benefits to organizations, enabling them to better protect against sophisticated cyber threats and improve their overall security posture. Let’s explore these benefits in detail:

Drastically reduced attack surface
The Zero Trust model eliminates the traditional perimeter concept, where trust is granted by default to users and devices within a defined network. Instead, it establishes a posture of “distrust by default”, where every access to resources is rigorously evaluated and permanently authenticated.
This approach eliminates the notion of static trust zones, thereby significantly reducing the attack surface that cybercriminals can exploit. An attacker who has successfully penetrated the network can no longer move freely and access sensitive data, limiting potential damage.
Strengthened data protection
Protecting critical data is at the heart of the Zero Trust philosophy. Indeed, this model puts granular controls in place to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a crucial role in adding additional layers of security to the login process. Additionally, role-based access control (RBAC) helps limit data access based on each user’s business needs. Finally, data encryption, both at rest and in transit, guarantees the confidentiality of sensitive information even in the event of compromise.
Improved intrusion detection and incident response
Zero Trust promotes continuous monitoring of user and device activities within the network. This granular monitoring makes it possible to quickly detect deviant or malicious behavior, such as unauthorized access to sensitive data or attempts to exfiltrate data.
Implementing incident detection and response solutions (SIEM) makes it possible to automate the analysis of activity logs and alert security teams in the event of suspicious anomalies. This proactive approach helps limit the impact of cyberattacks and speed up response times.
Increased compliance
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, has become a necessity for organizations. Zero Trust provides a robust framework to meet these requirements by ensuring the protection of sensitive data and effectively managing access to resources.
Granular documentation of user access and activities, as well as implementing strict access controls, facilitates compliance audits and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to data protection.
Increased adaptability to cloud and hybrid environments
In cloud and hybrid environments where resources and users are dispersed across multiple locations and platforms, security management becomes more complex. Zero Trust is particularly suited to these dynamic environments thanks to its approach focused on identity and continuous verification.
Every access to resources, whether it is a cloud application, an on-premises server or a mobile device, is evaluated based on the identity of the user, their device and associated permissions . This flexible approach ensures consistent security no matter where resources or users are located.
Improved user experience
Unlike traditional perimeter-based security approaches, Zero Trust can provide a smoother, more transparent user experience. This is because authorized users can access the resources they need without facing unnecessary friction, such as repeated login prompts or arbitrary access restrictions.
Centralized authentication system and role-based access policies allow users to seamlessly log in from any authorized device, without compromising security.
Flexibility and scalability
Zero Trust model provides a flexible and scalable architecture that can adapt to the changing needs of an organization. New resources, such as cloud applications or IoT devices, can be easily integrated into the Zero Trust environment without compromising overall security.
Reduced security costs
By consolidating security tools and streamlining access management processes, Zero Trust can help reduce security-related operational costs. Additionally, proactively preventing cyberattacks can result in significant savings in recovery and repair costs.
Improved safety culture
Zero Trust encourages a culture of security within the organization by making employees aware of cyber risks and empowering them to protect data. Regular training and security awareness programs can further strengthen this culture.
Despite its many benefits, implementing a Zero Trust approach requires careful planning and consideration. It is important to clearly define security objectives , identify critical resources and implement the appropriate technologies and processes.
However, for organizations looking to improve their security posture in the face of evolving cyber threats, Zero Trust offers an effective and robust approach to protecting their data and systems.
