Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
Dans cet article de blog dédié au règlement DORA, nous allons vous expliquer ce que c’est, ce qu’il va changer pour le secteur financier et comment ces institutions doivent s’y préparer.
In January 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) will be introduced and will apply to all financial institutions in the European Union.
In this blog post dedicated to the DORA regulation, we will explain what it is, what it will change for the financial sector and how these institutions must prepare for it.
What is DORA ?
In January 2023, a new regulation has been adopted within the European Union, the DORA. DORA is related to Information and Communication Technologies (ICT).
This regulation aims to improve the IT operational resilience of financial institutions by installing a system of governance and internal control.
With this law, the EU wants financial structures to reduce the risks linked to the growing dependence on ICT and third parties for critical operations.
Thus, the concept of operational resilience requires organizations to be ready to face incidents and to ensure the continuity of critical services and activities essential to the proper functioning of institutions and thus minimize disruptions for the financial system as well as for customers.
Organizations must therefore be able to “resist, react and recover” from the consequences of ICT incidents.
This therefore requires establishing strong security controls on systems, tools and third parties, implementing continuity and survival plans in the event of incidents and testing their effectiveness.
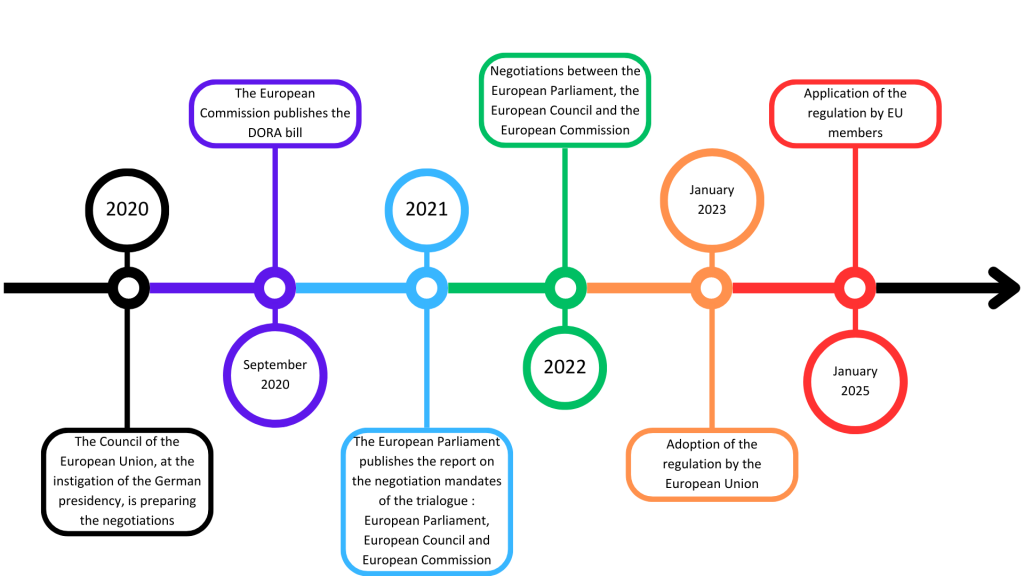
To whom does the DORA regulation apply ?
The DORA regulation aims to harmonize and unify European standards and requirements. Thus, it will affect and impact many financial institutions.
It will apply, among other things, to :
- Credit institutions
- Payment institutions
- Cryptocurrency establishments
- Crypto-asset service providers
- Investment institutions
- Insurance companies (& reinsurance)
- Management companies
- ICT service providers
The text of the law covers 21 categories of financial sector institutions, for a total of over 22,000 entities within the EU itself.
What does DORA change for financial institutions ?
This new regulation is based on 5 essential pillars of digital operational resilience. Financial organizations will have to implement them.
The 5 pillars of the DORA regulation
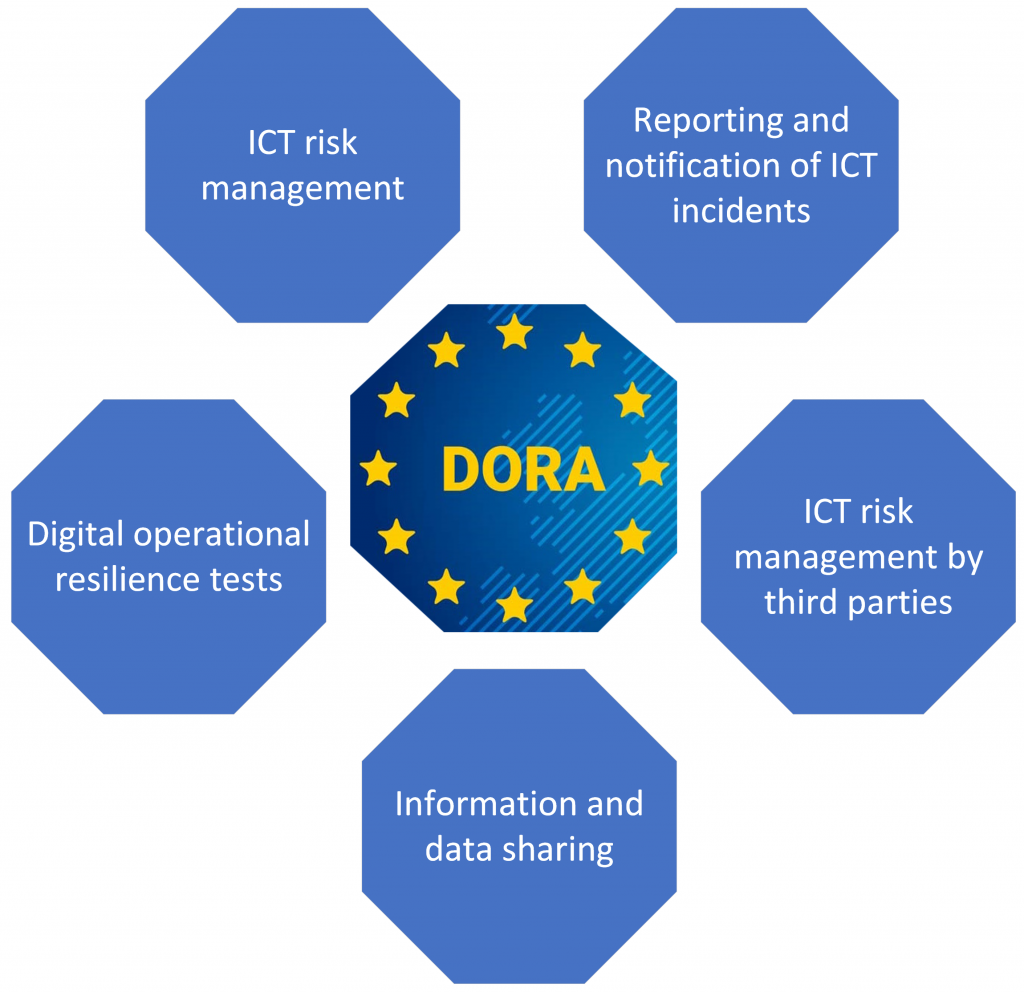
ICT risk management
Financial institutions are required to have an ICT risk management system in place. This system must be complete, efficient, secure and documented.
This guarantees a high level of digital operational resilience and thus protects against risks efficiently and effectively.
Companies will have to :
- Identify their tolerance for ICT-related risks.
- Create and apply risk management including identification of critical functions and associated risks.
- Implement specific risk prevention, detection, protection, response and recovery plans.
- Develop continuous improvement measures.
- Establish a crisis communication strategy with the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder.
- Train employees on digital operational resilience.
The management body bears the ultimate responsibility for managing the ICT risk of the financial institution.
Reporting and notification of ICT incidents
Financial institutions have an obligation to harmonize and centralize ICT incident notifications.
Entities must :
- Record and classify all ICT incidents and significant cyber threats according to the criteria detailed in the DORA regulation.
- Report, to the members of the management body, major incidents related to ICT.
- Report these incidents to the competent authorities.
- Create follow-up reports after one week and after one month after the incident.
Digital operational resilience tests
Financial institutions will :
- Create a comprehensive testing program, including assessments, methodologies, tools and practices.
- Test critical Information Systems (IS) for their protection and operational resilience.
- Run an intrusion test, or Pentest, based on threats (red team type) at least every 3 years on production systems. A certificate of conformity will be issued at the end of the Pentest.
ICT risk management by third parties
The management of risks related to third-party ICT service providers is fully taken into account in the new DORA regulation.
Thus financial entities are obliged to :
- Keep a register compiling all contracts and agreements, specifying those that affect vital or critical functions.
- Limit contractual requirements for increased third-party risk monitoring.
- Define a plan in terms of risks related to third-party providers.
Critical suppliers undergo annual assessments of resilience requirements such as availability, continuity, data integrity, physical security, risk management processes, governance, reporting, portability and testing.
These assessments are conducted directly by regulators and are subject to penalties for non-compliance.
Information and data sharing
The DORA regulation specifies the outline for the establishment of information sharing between institutions for cyber threats.
This type of process will allow companies to better prepare for cyber-attacks, and thus develop the detection and defense capabilities of financial entities.
How should financial entities be prepared for the DORA regulation ?
Financial institutions will have to prepare quickly to be operational for January 2025.
Indeed, this new law requires major changes to these entities, thus will generate many costs and many operational changes.
We therefore advise institutions to :
- Find out as much as possible about the new regulation.
- Audit their entity to find out what needs to be changed or improved.
- Estimate the potential costs of the changes.
- Get ready and start complying
- Have technologies in place to protect against cyber threats, such as vulnerability scanners.
- Train employees in cyber-risks, we recommend going through PASSI-certified training organizations, such as Ziwit.
- Create and harmonize the sharing of information via secure protocols and tools.
- Identify third-party partners related to ICT.
- Review relationships with ICT partners.
- Test information systems and resilience capabilities.
- Make a Red Team penetration test with independent organizations.
- Develop a strong and efficient culture of digital operational resilience.
