Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
We will explain everything about Ransomware-as-a-Service, from its definition, to how to protect yourself from it, through how it works and concrete examples.
According to The State of Ransomware Report by Sophos, in 2022, 73% of French companies were affected by ransomware.
Part of this phenomenon can be explained by the ease with which cybercriminals can obtain Ransomware-as-a-Service.
RaaS currently accounts for 11% of all cybersecurity attacks.
We will explain everything about Ransomware-as-a-Service, from its definition, to how to protect yourself from it, through how it works and concrete examples.
What is Ransomware-as-a-Service ?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) can be compared to Software-as-a-Service.
Ransomware-as-a-Service is an illegal business model that allows anyone, in exchange for money through a subscription system, to use Ransomware variants.
This therefore allows novice hackers to carry out ransomware-type attacks without developing the virus.
As with SaaS, RaaS developers regularly release new versions of their software for their customers.
The system is well established and has, like legal e-commerce solutions, more or less expensive subscription models, granting more or less features such as a dashboard, and having detailed guides and a technical support in case of problem.
The developers of these RaaS therefore choose not to carry out attacks themselves, but rather to sell their viruses.
RaaS developers have learned that it is less risky and less burdensome to create malware and sell or rent it to less skilled hackers than to carry out the attacks themselves.
Ransomware-as-a-Service provides all the tools cybercriminals need to execute malware without advanced knowledge.
How does Ransomware-as-a-Service work ?
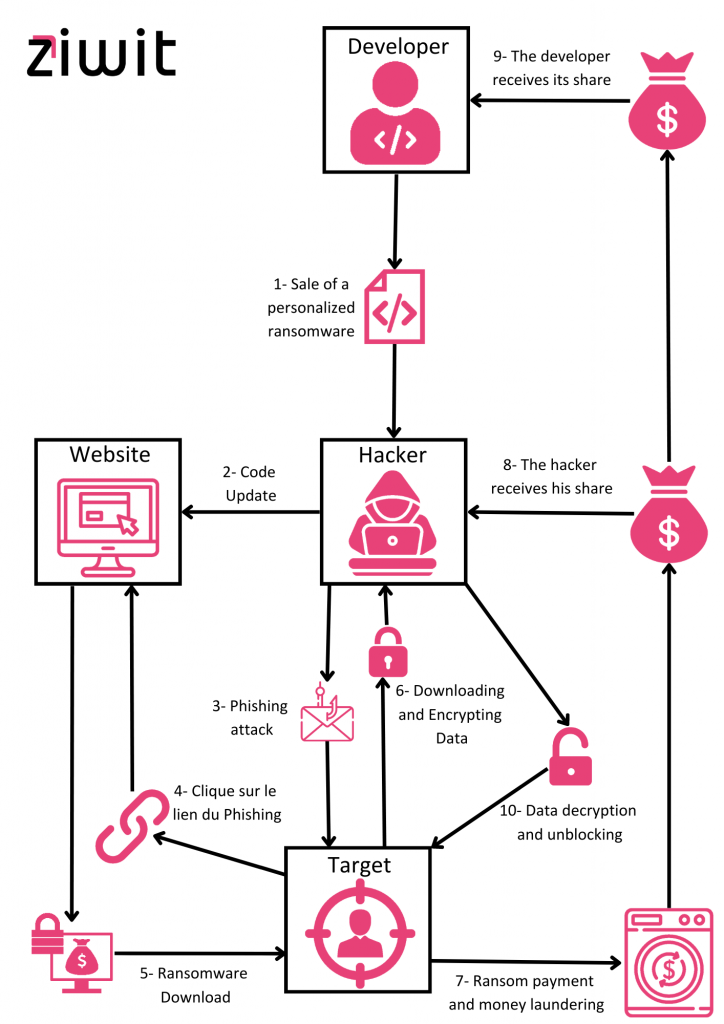
It all starts with the cybercriminal wanting to have a Ransomware, but his skills being limited, he will contact a RaaS developer to buy one.
On the Dark Web, several e-commerce sites offer RaaS for a fee.
There are several types of remuneration :
- Monthly subscription
- Participation on earnings
- One-time license purchase fee
Many RaaS developers will ask for additional information to accept or refuse the sale of their Ransomware.
Indeed, misuse of Ransomware can attract attention and harm the developer’s business.
The client will have to specify :
- The type of exploit wanted
- The type of encryption needed
- The targeted operating system
- The victims
- How much will the ransom be
- The text accompanying the ransom demand
The developer will then refuse or accept the client’s request. It will provide him a custom exploit code according to the criteria stated earlier.
Depending on the price paid / the subscription chosen, the customer will have more or less options as well as help such as technical support, a forum or tutorials.
Once the ransomware is acquired, the cybercriminal will then exploit it through phishing campaigns or social engineering.
Creating and sending phishing emails does not require any special skills, and the methods used to trick email filters are constantly evolving.
The victim who clicks on the corrupted attachment will see his computer blocked. His data was stolen.
A dialogue box will then open so that the cybercriminal can communicate with the victim.
The victim will have the choice to pay or not.
- If the victim wants to pay, then a payment portal will open and the victim will receive a decryption key with instructions on how to recover their files, but there is no guarantee that a decryption key will be sent to the victim.
- If the victim does not pay, then the data has a high chance of being sold on the Dark Web.
Examples of Ransomware-as-a-Service
DarkSide
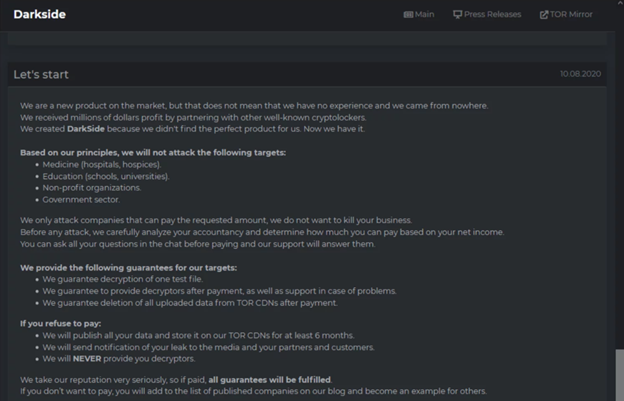
In 2021, DarkSide ransomware was used to steal 100 GB of data from network of Colonial Pipeline.
The company paid the sum of 5 millions dollars to recover his data.
The attack was perpetrated by a cybercriminal who acquired DarkSide ransomware from Carbon Spider developers.
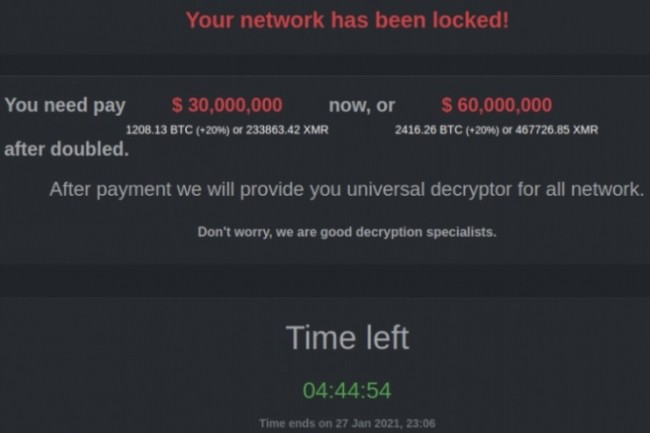
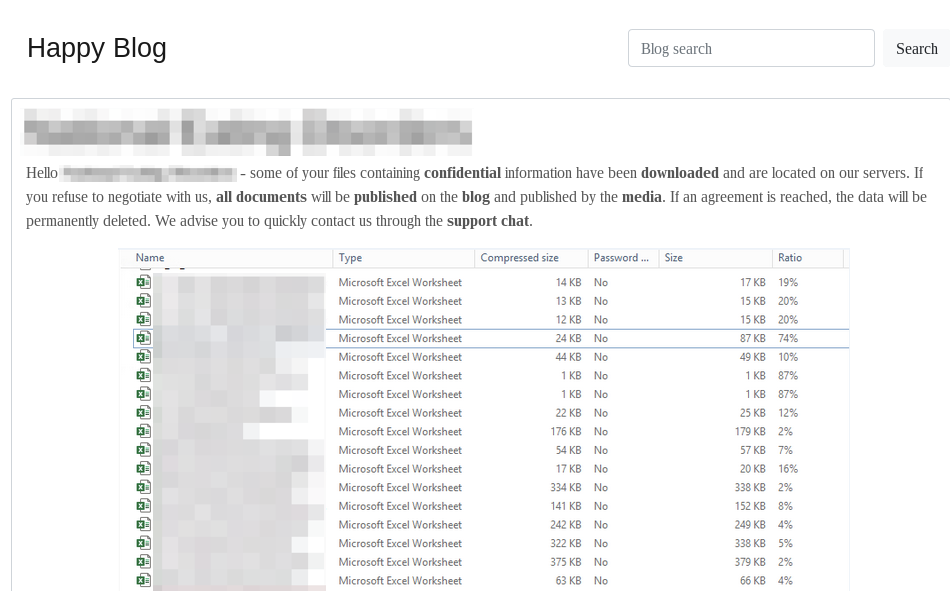
REvil
Pinchy Spider has designed a ransomware named REvil.
Their business model is attribution, developers take 40% of earnings.
In 2021, the IT provider Kaseya suffered a ransomware attack.
To find their data, the company paid 10 million dollars.
The operation of Pinchy Spider is simple. The developers notify their victims of the planned data leak via the publication of a blog post containing sample data as evidence, before disclosing the bulk of the data after a certain period of time. The REvil ransomware attaches a link to the blog post to the ransom note.
LockBit
LockBit, ransomware of Russian origin, has generated more than 1,700 attacks since 2020.
He was behind cyberattacks by large companies such as Continental or Thales.
In 2022, it becomes the most active ransomware with around 200 monthly attacks carried out by LockBit RaaS customers.

Responding to Ransomware-as-a-Service
It is essential to protect against Ransomware-as-a-Service.
Limit the risks
It is primordial to limit the risks of cyberattacks and ransom demands. To do this, here are several best practices :
Do updates
Hackers can exploit unpatched flaws in software.
The publishers of its software frequently offer updates preventing vulnerabilities from being exploited.
It is therefore strongly recommended to update the software as soon as possible to avoid and limit this kind of cyberattack.
Backups
Ransomware steals data from organizations and prevents them from using it.
Performing frequent backups on a separate, non-networked device helps restore data quickly without having to pay the ransom demand.
Train employees
Training is essential in preventing these attacks.
This is why Ziwit offers classes to raise awareness of computer security issues, threats and risks, as well as cybersecurity training to learn all the methods guaranteeing the security of networks, websites and other information systems.
Make a personalized phishing campaign
Phishing is a method used by cyber criminals to trick users.
Phishing campaigns are often used to steal data, spread computer viruses, extort money or infiltrate computer networks.
Cybercriminals mostly send fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from legitimate sources, tricking users into entering their login credentials, clicking on malicious links, or downloading malware-infected attachments.
Companies can set up phishing campaigns to test the vulnerability of their employees and strengthen their IT security.
The purpose of these phishing campaigns is to validate the level of maturity of your employees, in relation to a concrete and realistic case, but above all to raise their awareness through action.
Segment the network
Network segmentation greatly limits the proliferation of cyber attack in the environment.
Use a vulnerability scanner
Malware and ransomware infiltrate networks through several methods, including the exploitation of security vulnerabilities.
It is very strongly recommended to use flaw detection solutions such as a vulnerability scanner, HTTPCS Security for example.
This kind of tool automatically detects the vulnerabilities present and offers corrections. It has become essential in computer security today.
Detect a possible data leak
It is also highly recommended to have a Cyber Threat Intelligence solution.
The HTTPCS CYBERVIGILANCE solution constantly monitors the web, Deep web and Dark web networks to collect information concerning an organization and alert the impacted teams in real time.
What to do after a cyberattack?
If you have received a ransom note, you have probably been attacked. It is essential to react well and not to panic.
Here is a list of tips to try to get out of it as best as possible :
- Identify how and where you were attacked.
- Isolate the infected system as quickly as possible to limit the spread as much as possible.
- The French government recommends to NEVER pay the ransom. Indeed, you have no guarantee of finding your data and you have no guarantee that criminals will not seek to resell them on the Dark Web afterwards.
- If personal data has been stolen, it is MANDATORY to inform the CNIL as soon as possible, under risk of a fine.
- Learn from your mistakes by strengthening your IT security, training your employees and performing a Pentest, or intrusion test, to highlight existing IT security flaws.
