CyberNews May 2024
Discover the CyberNews of May 2024. This is the recap of news and current affairs on Cybersecurity during the month of May 2024 !
Discover the CyberNews for May 2024. This is the recap of news on Cybersecurity during the month of May 2024 in France.
Operation “Endgame”
Operation Endgame, carried out between May 27 and 29, 2024, was a large-scale international collaboration aimed at dismantling infrastructure, arresting cybercriminals and neutralizing large-scale malware.
This unprecedented operation mobilized the authorities of several countries, including France, Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, the United Kingdom and the United States, and dealt a major blow to the malicious actors operating in the cyberspace.
Ambitious objectives, concrete results
Operation Endgame had specific objectives:
1. Dismantling cybercriminal infrastructures
Authorities have targeted the networks and servers used by cybercriminals to host their malware, carry out their attacks and distribute their illicit profits. The operation targeted the “Bumblebee”, “Pikabot”, “Smokeloader”, “System BC”, “IcedID” and “Trickbot” infrastructures.

2. Malware neutralization
The operation helped neutralize several notoriously dangerous malware, such as Emotet, TrickBot and Dridex, which were responsible for a large number of infections and financial damages.
3. Searches and arrests of cybercriminals
Coordinated actions led to:
- 4 arrests: 1 in Armenia and 3 in Ukraine.
- 16 searches: 1 in Armenia, 1 in the Netherlands, 3 in Portugal and 11 in Ukraine.
The administrator of the Pikabot botnet was arrested in Ukraine with the assistance of Ukrainian authorities, one of the actors of the “Bumblebee” dropper was questioned in Armenia.

Face of world’s most wanted cybercriminal revealed
Dmitry Khoroshev, known as LockBitSupp, is the leader of the LockBit ransomware gang, considered one of the most dangerous in the world. On May 7, 2024, American, British and European authorities jointly revealed his identity in a major international operation.

“Khoroshev, aka LockBitSupp, who lived in anonymity and offered a $10 million reward to anyone who revealed his identity, will now be subject to a series of asset freezes and travel bans.”, we can read on the NCA website.
LockBit hacker group
Operation Cronos
Operation Cronos, a large international operation carried out on February 20, 2024, dealt a significant blow to the LockBit ransomware group.
This collaboration, involving 10 countries including France, the United States, Japan and the United Kingdom, made it possible to dismantle a significant part of the cybercriminal group’s infrastructure.
The return of Lockbit
LockBit is responsible for numerous high-profile cyberattacks, notably against the Cannes hospital in France on April 16. This cyberattack resulted in the paralysis of its computer system for several days.
The group is also known for targeting healthcare companies, causing significant financial and operational damage to its victims.

BreachForums seized by justice
On June 2, 2024, the FBI and the United States Department of Justice announced the seizure of the website BreachForums, an online marketplace infamous for the sale of hacked data, malware, and other cybercriminal acts.
According to authorities, BreachForums was run by a hacker known as “ShinyHunters” since June 2023. The site served as a hub for the sale of a wide range of illicit products, including:
- Stolen credentials, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers.
- Hacking tools and malware.
- Hacked databases containing sensitive information.
- Illegal services, such as denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and money laundering services.


Data leak of 560 million Ticketmaster customers
Ticketmaster is a multinational ticketing and entertainment company. It is one of the largest ticket sellers in the world, for concerts, sporting events, shows and other live events.
Ticketmaster data breach affects a staggering 560 million users worldwide, making it one of the largest data breaches on record. This means that the personal information of a large portion of concert and sporting event-goers is now compromised.
Ticketmaster Data Theft
- The data breach was discovered in May 2024, but Ticketmaster did not notify customers until June 2024.
- Compromised data includes names, email addresses, phone numbers, dates of birth, passwords and information partial on credit cards.
- The flaw is linked to an infiltration of the cloud provider Snowflake, used by Ticketmaster.
- The hacker group ShinyHunters claimed responsibility for the breach and put the stolen data up for sale on the dark web, on the site BreachForums, which did not remain seized for long.

Over $300 million in BTC stolen from Japanese exchange DMM Bitcoin
Japanese cryptocurrency exchange DMM Bitcoin suffered a major security breach in late May 2024, which resulted in the theft of 4,502.9 bitcoins (BTC), worth approximately $305 million at the time of the attack.
According to reports, the funds were transferred out of the exchange to unknown wallets around 1:26 p.m. (local time) on Friday, May 31. DMM Bitcoin detected the flaw and took steps to prevent further unauthorized withdrawals.
Despite these efforts, the hackers managed to flee with the stolen funds. DMM Bitcoin said it would work to refund its customers and had already started discussions with security companies to investigate the incident and strengthen its security measures.

Data breach of 49 million Dell customers
On May 9, 2024, Dell notified customers of a data breach that compromised the personal information of 49 million customers worldwide.
The breach was discovered after Dell received emails from hackers claiming to have access to the data. Although Dell has not confirmed the truth of these claims, the company has taken steps to secure its systems and has begun notifying affected customers.
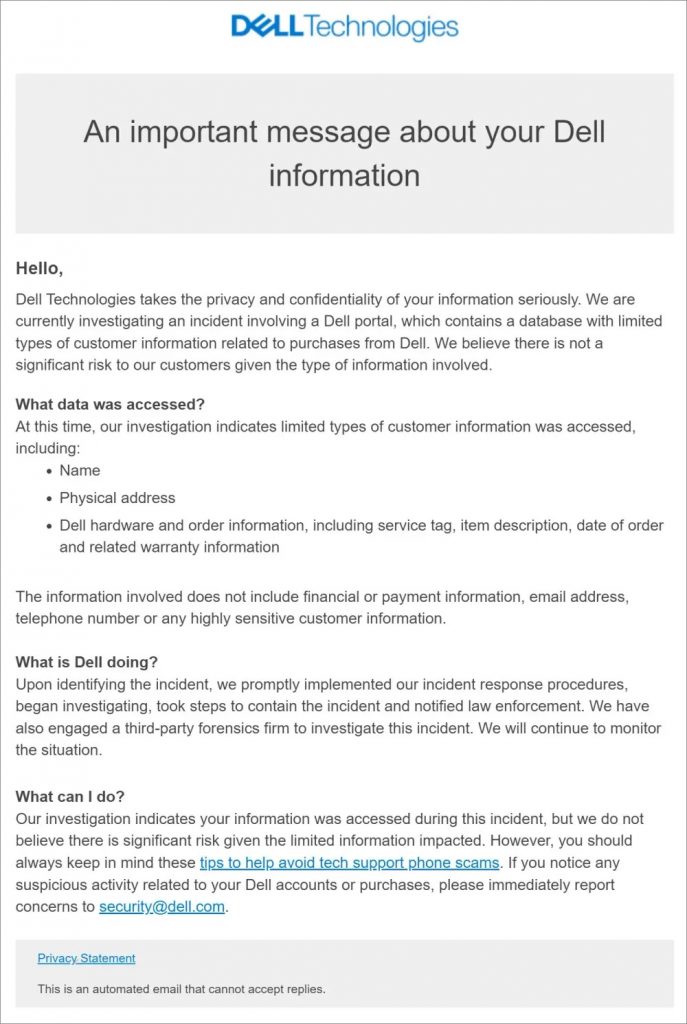
Compromised data includes:
- Names,
- Addresses,
- Details on PC purchases,
- Warranty information,
- Service labels.
Dell said there was no evidence that financial data or passwords were compromised. However, the company encourages customers to change their passwords as a precaution.
The breach is apparently the result of an abused API. APIs are interfaces that allow different applications to communicate with each other. In this case, hackers allegedly abused a Dell API to access customer data.
Dell takes the data breach seriously and has implemented a number of measures to improve its security. The company also set up a website and hotline to answer customer questions.

Cyberattack on the CCI Pau Béarn
On May 13, 2024, the Pau Béarn Chamber of Commerce and Industry (CCI) was the target of a cyberattack. This attack hit the Pau-Pyrénées airport and the Pau business school.
Valérie Duboué, general director of the CCI, declared: “The activity continues, the planes take off and land at Pau airport […] Obviously, the fact of suffering a cyber attack disrupts normal activity a little but the Most of the activity is going very satisfactorily. We know that this is often the goal, to extort money from people or organizations that have been attacked, but there is no very clear ransom demand.”
The CCI reacted quickly to the attack by filing a complaint and putting in place measures to limit the damage. Computer systems were gradually restored and services returned to normal.
The MONTI cybercriminal group
Behind this cyberattack is the cybercriminal group MONTI.
On May 26, 2024, thousands of confidential documents, stored on the dark web since May 23, were released by the hacker group.
Among these documents are sensitive airport files, such as:
- “garage”,
- “schedule”,
- “customer complaints”,
- Plus crucial information on cybersecurity, security and access badges.
The ESC de Pau, also a victim of this cyberattack, saw the data of more than 2,200 students and employees exposed. This information includes:
- Diplomas,
- Tuition,
- Administrative files.

Data leak within the German army
In early May 2024, a major security breach hit the German military, exposing sensitive information on thousands of military meetings.
Webex videoconferencing platform, allowed hackers to access details concerning at least 6,000 meetings, some of which were classified confidential.
The compromised information included:
- Dates,
- Hours,
- Places,
- Lists of meeting participants.
In addition, some documents shared during these meetings were also allegedly hacked. The meetings focused on sensitive subjects such as: the long-range Taurus missiles claimed by Ukraine or “the digital battlefield”.
This data leak caused shock waves within the German army and raised serious concerns about the security of military communications.
Several factors contributed to the severity of this security breach. First, Webex , the video conferencing platform used by the German military, was not properly configured, making it easier for hackers to gain access. In addition, the German army would not have sufficiently protected the sensitive data shared on the platform.
Questioned by AFP, a spokesperson for the Bundeswehr’s “cyberspace and information” command confirmed that the army’s Webex instance “presented a flaw” and that once it was known, it was corrected “within due time.”24 hours”.

Qnap products
Major flaws discovered in Qnap NAS software pose an imminent danger to the security of data stored on these devices. If these flaws were exploited by malicious individuals, the consequences could be disastrous:
- Unauthorized access and remote takeover of NAS: Imagine a hacker able to break into your NAS, like a digital thief breaking into your safe. Your confidential data, your precious photos, your professional documents, everything would be at his mercy.
- Theft of sensitive data: Your customer lists, your financial reports, your current projects… A real treasure for cybercriminals who could resell them to the highest bidder on the black market, causing you immense financial and reputational damage.
- Spying and surveillance: Camera connected to your NAS? The hacker could take control of it, turning you into an unconscious victim of unwanted surveillance.
- Data Destruction: Out of revenge or to sow chaos, the hacker could wipe out your files, depriving you of irreplaceable memories and causing serious operational harm.
Qnap NAS affected by these critical flaws are as follows:
- QTS 5.x, 4.5.x
- QuTS hero h5.x, h4.5.x
- QuTScloud c5.x
- myQNAPcloud 1.0.x
- myQNAPcloud Link 2.4.x
- Media Streaming Add-on 500.1.x
It is important to update your Qnap NAS with the security patches made available by Qnap.

Vulnerabilities in Check Point VPNs
On May 30, 2024, CERTFR published an alert regarding a critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-24919) affecting Check Point VPN and Firewall products.
This vulnerability allows an authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code on the targeted device, giving them full control over the device.
Since late April 2024, malicious actors have been actively exploiting a critical zero-day flaw (CVE-2024-24919) affecting Check Point VPNs. This flaw allows hackers to remotely access corporate networks by compromising Check Point firewalls, exposing sensitive data and endangering IT systems.
Check Point released an urgent security patch on May 25, 2024, but attacks are still ongoing and hackers are actively exploiting this flaw. It is crucial for organizations using Check Point VPNs to take immediate steps to protect themselves.

Cyberattack in Helsinki
A large-scale cyber attack recently hit the city of Helsinki, compromising the personal data of 80,000 students and 40,000 municipal employees. This data breach is one of the largest ever to occur in Finland and raises serious concerns about the security of personal information.
This computer attack hit the educational network of the city of Helsinki, affecting students from kindergarten to high school.
According to Jussi Eronen, an official at the National Cybersecurity Center, the attack exploited a security flaw in a server connected to the network. This has allowed cybercriminals to access a wide range of sensitive data, including:
- Lastnames and firstnames,
- Email addresses,
- Identification numbers,
- Information regarding legal representatives of students.
In addition to student data, the hackers also stole the usernames and email addresses of all municipal staff. Among the compromised information, some contain confidential or sensitive data, such as medical certificates or work stoppages.

The University of Guyana victim of a cyberattack
The University of Guyana was indeed the victim of a cyberattack on Tuesday April 30, 2024. This attack had the following consequences:
- Encryption and/or erasure of certain university files. This disrupted the operation of several digital services, such as the Moodle educational platform, website and email.
- Broadcasting music videos and war footage on the university’s YouTube channel. Local authorities suspected infiltration for Russian propaganda purposes.
Actions taken by the University
- Shutdown of affected computer systems. This helped limit the scale of the attack and protect the remaining data.
- Implementation of a data restoration plan. The university worked with cybersecurity experts to recover the encrypted files.
- Filing a complaint with the authorities. An investigation is underway to identify the perpetrators of the attack and bring them to justice.
- Implementation of new security measures. The university has strengthened its IT systems to better protect against future attacks.
Impact of the attack
The attack caused significant disruption within the university. Students and staff have had difficulty accessing essential digital services. The university also suffered significant financial harm.

A million washing machines hacked by students
In May 2024, two computer science students from the University of California at Santa Cruz, Alexander Sherbrooke and Iakov Taranenko, discovered a major security flaw in the connected laundromat management system of the company CSC ServiceWorks. This flaw allowed them to take remote control of more than a million washing machines around the world, and use them for free.
Flaw and impact
Students exploited a flaw in the system’s API CSC ServiceWorks, which allowed washing machines to be accessed and controlled remotely. Using this flaw, they were able to unlock machines, run wash cycles, and even change configuration settings.
This flaw affected a wide range of connected washing machines, installed in laundromats, university residences and rental accommodation. Students Estimated More Than 1 Million Machines Vulnerable in around twenty countries.
The students initially attempted to alert CSC ServiceWorks of the security breach, but the company did not respond. So they decided to publicly disclose the flaw, in order to force the company to take action.

Google Data Leak
May 2024 saw a major data breach at Google, exposing thousands of internal documents from the company’s research team. This revelation was made public by SEO specialist Rand Fishkin.
At the heart of the leak are 2,500 pages of documents detailing various aspects of the inner workings of Google’s search algorithm.
Leaks of these documents
- Detailed guidelines for Google’s search quality raters, which provide an overview of the criteria used to judge the relevance and usefulness of web pages.
- Internal communications on SEO strategies, offering a look at how Google thinks about optimizing its own content for search.
- Discussions about Google’s competitors, highlighting the company’s perceptions and approaches to players like Amazon and Bing.
Some experts say the documents reveal a bias toward Google products and services in search results, which could have anticompetitive implications. Others fear the leak could expose search manipulation tactics, undermining confidence in the integrity of Google’s ranking process.
Google responded to the leak by saying it was investigating the matter and taking steps to protect its confidential data. The company also emphasized that its guidelines for search quality raters are regularly updated and that its search algorithms rely on a variety of signals to rank web pages.

4 critical flaws affect Aruba equipment
4 critical security vulnerabilities were recently discovered in Aruba devices, allowing malicious actors to execute code remotely.
These flaws, identified under the references CVE-2024-26305, CVE-2024-26304, CVE-2024-33511 and CVE-2024-33512, are linked to buffer overflows in the PAPI (Performance Application Programming Interface).
By exploiting these vulnerabilities, an attacker could take full control of a targeted Aruba device remotely. To do this, it would simply send a specially crafted PAPI request to port 8211 in UDP.
Aruba has already released patches for these critical flaws. It is strongly recommended to apply these patches as soon as possible to protect your devices from attacks.
