Steganography & Cyberattacks
Steganography in cyberattack makes it possible to hide malware, exfiltrate data or communicate discreetly by hiding messages in innocent files.
Steganography, from the Greek ” steganos ” (hidden) and ” graphein ” (to write), is the art of hiding information in a seemingly innocuous covering medium, such as an image, an audio file or ordinary text.
The objective is to make the secret message invisible to the naked eye, while making it accessible to a recipient who has the key to decode it.
Once used by spies and dissidents, it is now exploited by cybercriminals for stealthy and sophisticated attacks.
How does Steganography work?
Steganography is based on the principle of hiding a secret message in a covering medium. This medium can be a text file, an audio image, a video or a digital image.
The goal is to modify the cover media in a way that is undetectable to the human eye, while still inserting the secret message.
Here are some common steganographic techniques:
Least significant bit (LSB) steganography
This technique consists of modifying the least significant bits of pixels in an image to encode the secret message. As the human eye is not very sensitive to variations in low order bits, these modifications generally go unnoticed.

The image above shows an example of Least Significant Bit Steganography (LSB).
Here, the last bits of each color square have been changed, without this having any visible impact on the final result.
The changed bits form a word, in our example, CAT.
Overlapping Steganography
This technique consists of superimposing the secret message on the cover material so that it is invisible to the naked eye. This can be achieved using digital watermarking techniques or by modulating the transparency of the secret message.
Substitution steganography
This technique consists of replacing part of the cover material with the secret message. For example, we can replace random characters in a text file with bits of the secret message.
Empty space technique
In audio or video files, there are often unused spaces that can be exploited to hide data. For example, you can slightly increase the duration of a silent pause in an audio file to encode a message.
Steganography by file structure
File structure-based steganography uses unused spaces for content hiding.
Uses of Steganography
Steganography, the art of hiding secrets, offers a range of applications well beyond espionage and coded messages. Here are some concrete examples of its use in the modern world:
1. Protection of intellectual property
- Fight against piracy: Integrating digital watermarks into images, videos and music makes it possible to trace the origin of pirated content and fight against its illegal distribution.
- Document authentication: Inserting a unique steganographic mark into digital documents guarantees their authenticity and prevents falsification.
2. Discreet communication
- Investigative journalism: Journalists can hide sensitive information in innocent files to communicate it securely.
- Political dissidents: In repressive regimes, steganography allows citizens to share information and dissenting opinions without arousing suspicion from authorities.
3. Image enhancement
- Image enhancement steganography: This technique allows additional information to be inserted into digital images, such as detailed descriptions for visually impaired people, without visibly altering the image quality.
- Conservation and restoration of works of art: Steganography can be used to store information on the original state of a work of art or to document the stages of its restoration, thus allowing better preservation of artistic heritage.
4. Awareness
- Awareness campaigns: Concealing awareness messages about social issues in popular media, such as posters or videos, can reach a wide audience in a subtle and effective way.
5. Scientific and research areas
- Transmission of scientific data: Researchers can use steganography to share sensitive or confidential data with each other securely.
- Psychology experimentation: Steganography allows subliminal stimuli to be introduced into images or videos to study their impact on human behavior.
How do cybercriminals use Steganography?
In the field of cybercrime, steganography has become a tool favored by criminals. Indeed, this technique offers cybercriminals a sneaky way to hide malicious data, steal sensitive information and bypass security systems.
Here are some concrete examples of the use of steganography by cybercriminals:
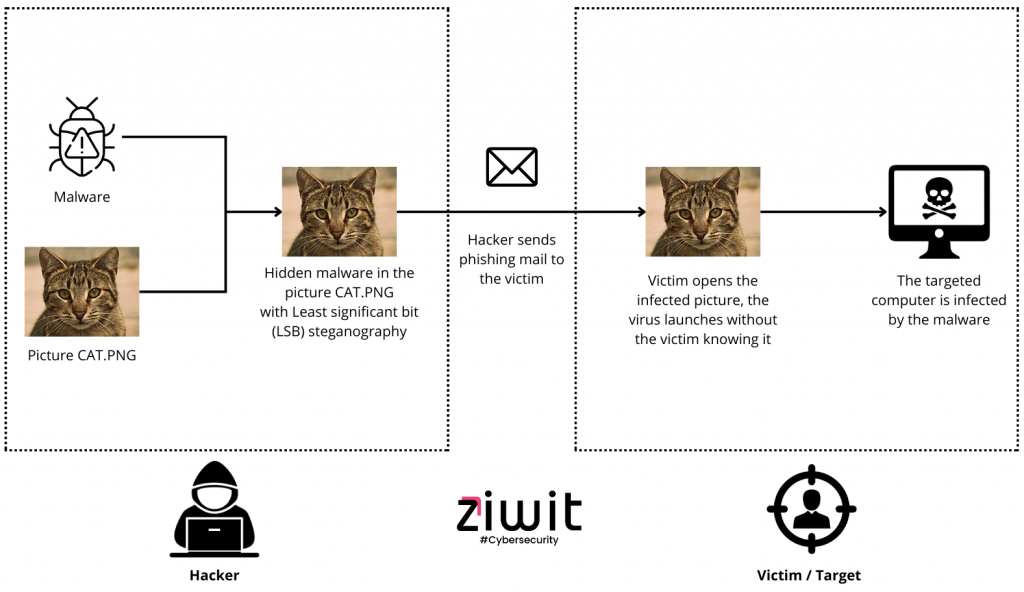
1. Dissemination of malware
- Hiding malware in images or audio files: Cybercriminals can hide malware in innocent files, such as images uploaded to websites or email attachments. Once opened, these files infect the victim’s device without their knowledge.
- Social media exploitation: Encoded messages or malicious links can be hidden in images or videos shared on social media, tricking users into downloading or clicking on them, thereby triggering the infection of their device.
2. Theft of sensitive data
- Exfiltration of confidential data: Financial information, personal data or trade secrets can be hidden in ordinary files, such as Word documents or PDF files, and sent to unauthorized parties.
- Corporate espionage: Malicious actors can use steganography to steal sensitive information about competitors by infiltrating internal files or intercepting communications.
3. Circumvention of security systems
- Spam filters: Spam messages or malicious links can be hidden in images or email attachments, fooling spam filters and reaching victims’ inboxes.
- Network Activity Hiding: Steganography allows malicious communications or illegal data transfers to be hidden in network traffic, thereby evading detection by security systems.
Examples of cyberattacks using Steganography
Steganography has unfortunately become a formidable weapon in the hands of cybercriminals. Here are some concrete examples:
1. Operation Windigo
In 2011, a group of cybercriminals used steganography to distribute a Trojan called ” Windigo ” via images uploaded to popular websites. The infected images, when opened, installed the malware on the victim’s device, stealing sensitive information.
2. Attacks on banking systems
In 2013, a steganographic malware campaign targeted banking systems. Hackers hid malware in PDF files emailed to bank employees. Once opened, these files infected banking systems, allowing hackers to steal financial information.
3. Phishing campaign
In 2016, a sophisticated phishing campaign used steganography to deliver malicious emails. The emails contained seemingly innocent images, but in reality, hid links to fraudulent websites. Once victims clicked on the links, their personal information was stolen.
4 . Ransomware attacks
In 2017, the “ SyncCrypt ” ransomware was distributed via email attachments containing steganographic images. Once opened, the ransomware encrypted the victim’s files, demanding a ransom to decrypt them.
These examples illustrate the diversity and complexity of steganography attacks. Cybercriminals continue to innovate their techniques, making detection and prevention of these attacks increasingly difficult.
Protect yourself against Steganography
Faced with this evolving threat, a multidimensional approach is necessary to protect ourselves effectively:
1. Increased vigilance and awareness
Be extremely cautious of suspicious files, especially those from unknown sources. Educate your employees and those close to you about the risks of steganography and best practices to protect yourself from it.
2. Specialized security solutions
Consider using software or tools specialized in steganography detection. These tools can analyze your files and identify the presence of hidden data.
Additionally, you can use website integrity software, it will check if files have been modified without your consent. This way, you are alerted when the slightest change is made to your site or web application that could prove dangerous or fraudulent.
3. Regular software updates
Make sure your operating system, antivirus software, and firewalls are up to date with the latest security patches. These updates often include protections against emerging steganographic threats.
4. Encryption of sensitive data
Encrypting your important files can make them more resistant to steganographic attacks. Indeed, even if hackers manage to hide malicious data in your encrypted files, they will not be able to read them without the decryption key.
5. Regular backups
Make regular backups of your important data. In the event of a successful steganographic attack, you will be able to restore your files from a clean backup.
6. Responsible online behavior
Be careful when sharing files online, especially on public forums or social networks. Avoid sharing sensitive information or confidential files that could be easily accessible to cybercriminals.
7. React quickly in the event of a proven attack
You have discovered that your site has been hacked, don’t wait any longer and call an Incident Response Team. It helps and supports you when your business has suffered a malicious attack.
