Cryptojacking: Cybercriminals at the heart of cryptocurrency mining
With a 43% increase in incidents between 2021 and 2022, the cryptojacking phenomenon has reached an all-time high. By the end of the year, a total of 139.3 million attacks had been recorded, surpassing the previous record of 100 million. These attacks have also expanded their scope to new regions, with a significant increase in Asia and Europe.
With a 43% increase in incidents between 2021 and 2022, the cryptojacking phenomenon has reached an all-time high. By the end of the year, a total of 139.3 million attacks had been recorded, surpassing the previous record of 100 million. These attacks have also expanded their scope to new regions, with a significant increase in Asia and Europe.
It should be noted that France represents nearly 6% of the total volume of cryptojacking attacks, representing a growing threat in the field of cybersecurity. In France, cryptojacking represents 5.9% of the total volume of attacks, which places France 4th in the world and 2nd in Europe in this field. Companies are also exposed to network interruptions and increased costs resulting from the intensive use of processors, particularly in the cloud.
According to Symantec’s report, the number of infected computers grew exponentially by 8 500% in 2017. It is also noted that France slightly reduced its overall cyber attack rate from 2.35% to 2,21% between 2016 and 2017.
Cryptojacking is a form of fraudulent attack aimed at illegitimately exploiting the computing power or bandwidth of a device, whether it is a computer or other device, for the purpose of undermining cryptocurrencies, without the consent or knowledge of the individual or organization concerned.
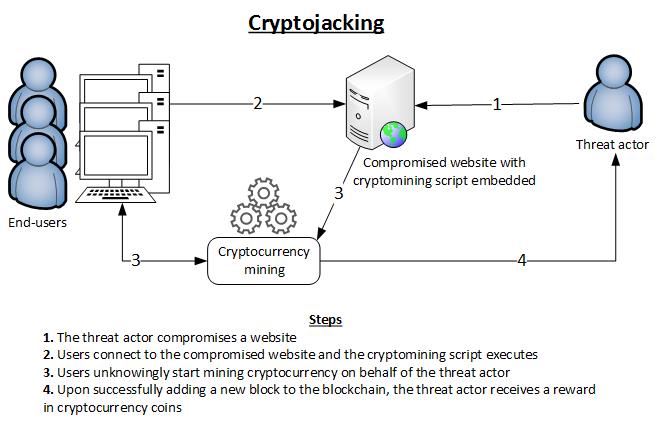
How does cryptojacking work?
Cryptojacking is closely related to the cryptocurrency mining process, which involves creating new units of cryptocurrency and adding them to a blockchain. Blockchain is a technology for continuously adding new blocks to a chain as users generate, spend, and transfer that currency. It is also used to track cryptocurrency transactions, identify owners and determine their value.

Miners need considerable computing resources to be the first to solve a mathematical problem. Originally, a user could mine cryptocurrencies using a desktop computer with a high-performance graphics card. However, nowadays it is necessary to have large-scale mining farms to produce cryptocurrencies at a sufficiently high frequency, thus allowing the miner to be remunerated for their time and the energy used to operate the equipment.
This is how cryptojacking affects both individual users and large corporations. When a computer is compromised, the main telltale sign is reduced system performance. At this point, a Trojan comes into play to exploit the computing capabilities of the device in the background.
The causes of cryptojacking
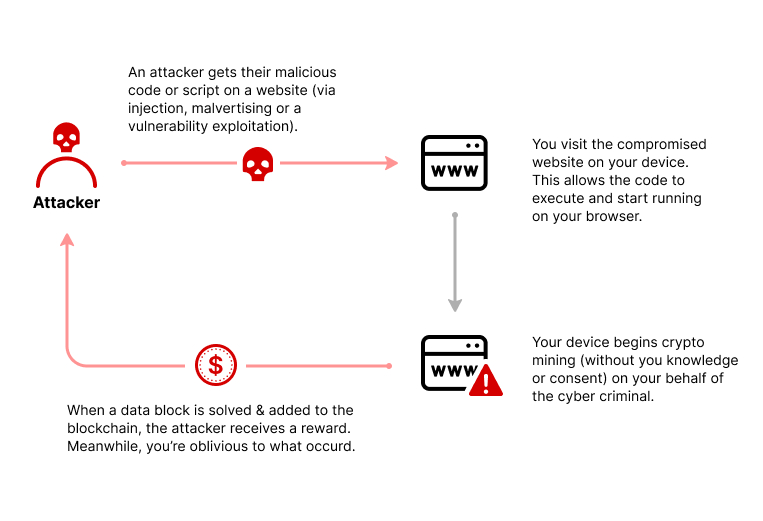
Indeed, cybercriminals have several methods to infect users’ devices and use them for cryptocurrency mining, without their knowledge.
These include:
Malware
Cybercriminals use malware such as ransomware to infect users’ devices. These malicious programs are often distributed through e-mail attachments, infected file downloads or compromised websites. Once installed on the device, this malware executes mining scripts in the background, without user’s consent.
Malicious websites
Some malicious websites embed mining scripts into their code so that when a user visits the site, their device begins to mine cryptocurrencies in the background, without their consent. Users may be directed to these malicious sites through deceptive links, fraudulent advertisements or phishing techniques.
Security flaws
Cybercriminals targetflaws in software, operating systems, or web applications to exploit them and install mining scripts on compromised devices. These security flaws may result from bad practice in the development of the web application, or negligence in updating software, for example.
Browser extensions
Malicious browser extensions can be downloaded and installed by users from untrusted sources. These extensions may contain mining scripts that run when browsing the Internet, thus using the resources of the user’s computer to mine cryptocurrencies without their knowledge.
The consequences of cryptojacking
The consequences of cryptojacking can be significant. First of all, the misuse of computer resources for mining purposes results in a slowdown of other processes running on the device. Thus, the computer’s responsiveness is reduced and its performance weaken in the accomplishment of daily tasks. Programs take longer to load, and web take longer to display, which significantly impairs the computing experience, leading to frustration and annoyance.
Besides this performance impact, cryptojacking can also have financial repercussions. Intensive use of a device’s computing capabilities leads to increased energy consumption. As a result, electricity bills exceed the norm, given that the device operates at full capacity to carry out cryptocurrency mining, even during periods of inactivity.
In addition, it is important to note that cryptojacking can also contribute to reducing the lifespan of a device. When hardware components, such as the processor and graphics card, are subjected to intensive and prolonged use, they are subject to an increased wear. This prolonged solicitation can accelerate the process component’s deterioration, leading to premature device failure. Therefore, it is possible to have to consider replacing the device earlier than planned, which generates significant additional costs.
The motivations of cybercriminals behind cryptojacking
Cryptojacking represents a financial advantage for cybercriminals, as they can generate revenue without incurring the costs of mining equipment, electricity, and maintenance, which is a significant expense for legitimate miners. By exploiting stolen resources, attackers maximize their gains while minimizing expenses.

Furthermore, cryptojacking has characteristics that make it less risky for attackers. Attackers conceal their malicious activity in various ways, making cryptojacking difficult to detect. Unlike more visible attacks, typical indicators such as decreased device performance can be attributed to other problems, which can delay discovery. In addition, the chances of prosecution are reduced, as it can be complex to trace the origin of the attack and identify those responsible. Cybercriminals may also operate from regions where cybercrime legislation is less strict, making prosecution more difficult.
Cryptojacking detection
Indeed, some warning signs may indicate the presence of cryptojacking. When a computer experiences significant slowdown, even when it’s not running resource-intensive programs, this can be an indicator of cryptojacking. Intensive use of resources can cause the device to overheat, which is another sign to look out for. When the processor and other components are running at full capacity for cryptocurrency mining, this can generate more heat, causing the device to overheat.
In addition, if the device’s cooling fan is spinning more often or louder than usual, this can also be a telltale sign of excessive resource usage. It is important to remain vigilant for these signs, and if cryptojacking is suspected, it is recommended to carry out a thorough antivirus scan and take the necessary steps to eliminate any malicious activity.
The HTTPCS vulnerability scanner can detect the use of web server resources for mining purposes (and more than 160,000 types of vulnerabilities or configuration problems).
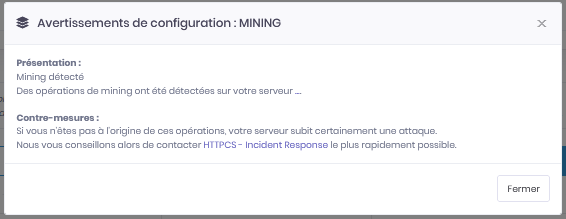
Cryptojacking Prevention
To protect against cryptojacking, there are several preventative measures to consider, including:
1. Implementation of security solutions in prevention
Including vulnerability scans to identify security flaws or misconfiguration enabling the installation of mining scripts, as well as malware detection tools to block cryptojacking programs.
2. Use of detection security software
Antivirus and antimalware programs are essential for detecting and blocking unauthorized mining scripts. They can identify known malware and prevent it from running on your system.
Ziwit can support you in setting up and managing your cybersecurity solutions, in particular through its Cybersecurity Operations Center.
At a higher level, you can detect the injection of suspicious scripts on your websites via website integrity solutions (Integrity Monitoring), which continuously analyzes the modifications affecting your websites.
3. Network Monitoring
Regular network monitoring is used to detect all suspicious activity or abnormal behavior that could indicate a cryptojacking attempt.
4. Regular updates and security patches
It is crucial to keep operating systems, browsers and other software up to date. Updates often contain security patches that close vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
A vulnerability analysis and obsolescence detection solution can help you to keep control of your websites and applications, for example.
5. User awareness
It is important to educate users about the risks of cryptojacking and provide training on good security practices. This may include advice on being careful when opening suspicious e-mails, avoiding downloads from untrusted sources, and being vigilant when browsing the Internet.
6. Avoid attachments from unusual or questionable email
Cybercriminals can use phishing e-mails to trick users into downloading corrupted programs or extensions. So, it is important to not open attachments from unknown or suspicious sources. Carrying out a phishing campaign to raise employee awareness can be an interesting action to implement.
7. Choosing a browser with an integrated anti-cryptojacking system or using a dedicated extension
Some browsers natively integrate devices for blocking cryptojacking scripts, such as Opera or Firefox. These tools block unauthorized mining scripts and add an extra layer of security.
8. Use of ad blockers
These browser extensions can detect and block cryptojacking scripts, providing an extra layer of protection and also preserving your privacy. Some web browsers, like Brave, natively integrate these cryptojacking script blocking features. Some antivirus software also includes cryptojacking detection and prevention features.
9. Block execution of JavaScript scripts
Blocking the execution of JavaScript scripts is a method to prevent malicious programs from taking advantage of your computing power. However, this approach may cause problems with legitimate websites that use JavaScript, as it may affect their normal operation.
10. System Performance Analysis
Regularly monitor the performance of your computer systems to detect any unusual slowdowns that may be the result of cryptojacking activity.
It is important to note that cryptojacking is often carried out illicitly. Because of this, users should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to protect themselves and stay vigilant as cybercriminals continually seek new ways to target users to maximize their profits.
